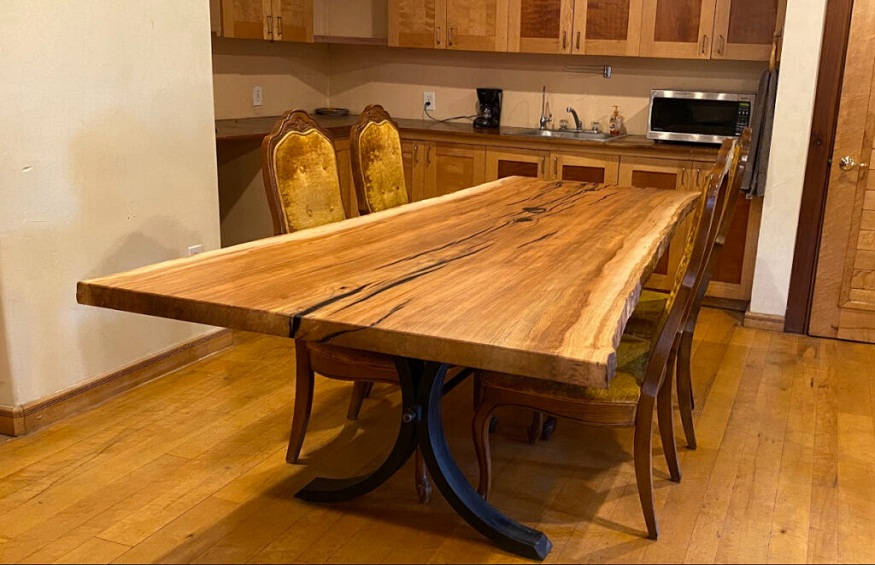
Is interior design your passion? If so, you’ve probably known about live edge furniture. You
HDFC Home Loan EMI Calculator allows calculating EMIs for Home Loan that further helps the
When it comes to protecting your home or building from water damage, one of the